MPEG-2 Intellectual Property Management and Protection (IPMP)
MPEG doc#: N7503
Date: July 2005
Author: JI Ming (Panasonic)
Introduction
MPEG-2 Part 11 is a specification on IPMP (Intellectual Property Management and Protection), which is a DRM (Digital Right Management) architecture developed by MPEG for MPEG-2 systems, based on MPEG-4 IPMP Extensions (MPEG-4 IPMP-X) architecture. MPEG-2 IPMP provides a normative framework to support many of the requirements of DRM solution: renewability, secure communications, verification of trust, granular and flexible governance at well-defined points in the processing chain, etc.
Why did MPEG-2 move from CA to IPMP?
While proprietary Conditional Access (CA) systems can be integrated with MPEG-2 audio/video technology, there are no provisions for achieving inter-working between different Conditional Access systems. The Simulcrypt system (defined in DVB), providing a limited form of interoperability in digital television, was integrated in using these “hooks” (and some further semantics defined in the European Digital Video Broadcast (DVB) project). It is also known that MPEG-2’s provision for CA system is not flexible, it has no support for CA system to perform watermarking or rights management, it has no support for multiple CA system to perform at the same stream simultaneously. It is also not secure enough, as it does not provide good renewability of CA system. The lacking of syntax for ECM and EMM also results in less interoperability.
It is also generally acknowledged that every DRM system is jeopardized to be broken, especially when the content is of high value. This is one of the serious problems encountered in digital content delivery business. It is therefore desired to establish a renewable DRM system. Furthermore, the need to deliver contents anytime, anywhere and to any device demands an international standardization effort.
During the progress of MPEG-4 IPMP Extension (MPEG-4 IPMP-X), the architecture and concept of it was also mapped to MPEG-2 system, which is called MPEG-2 IPMP. MPEG-2 IPMP is designed to address the above problems, in particular, renewability and interoperability, taking consideration of MPEG-2 system’s own nature.
MPEG-2 IPMP Architecture
The architecture for MPEG-2 IPMP terminal, and the key elements of MPEG-2 IPMP are similar to MPEG-4 IPMP-X. These can be found in the white paper for MPEG-4 IPMP-X.
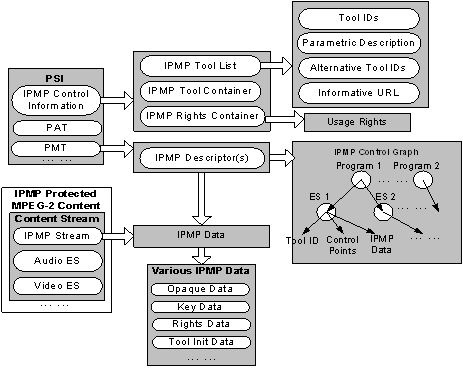
The following figure illustrates the structure of a MPEG-2 system content protected by MPEG-2 IPMP. The information contained in the IPMP Control Information Table and Content stream is shown and the relation between them is indicated.
Advantages of MPEG-2 IPMP
It is far beyond CA framework provided by the original MPEG-2 system, yet maintaining the compatibility. MPEG-2 IPMP offers the following advantages, which promotes secure globally content delivery anytime to any device.
- Interoperability: By using a common set of IPMP messages, and industry defined messaging API and messages extension, different IPMP Tools can be easily plugged into the terminal and interact with each other.
- Renewability: Through the usage of Tool List and IPMP Descriptor, one can easily renew a tool for better IPMP protection.
- Flexibility: MPEG-2 IPMP does not standardize the tools. One can choose whatever algorithms or tools to perform decryption, watermarking, user authentication or data integrity checking.
- Dynamic operation: Various IPMP Tools protection can be signaled in the content with the help of IPMP Descriptor, control point, sequence code. Different Tools can operate at the same or different control points, acting on the same or different streams.
- Secure tools: Terminal and Tools can choose to perform mutual authentication using IPMP messages.
- Forward and backward compatibility with existing Conditional Access system.
References
[1] ISO/IEC 13818-11, IPMP on MPEG-2 systems
[2] ISO/IEC 13818-1, GENERIC CODING OF MOVING PICTURES AND ASSOCIATED AUDIO: SYSTEMS
